
N2 + O2 -> 2NO
|
1 - Nitrogen and oxygen directly
combine inside the cylinders of the internal combustion engine producing
nitrogen oxide. |
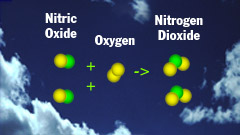
2NO + O2 -> 2NO2
|
2 - As soon as the nitric
oxide from the exhaust reaches the atmosphere, it is oxidized by oxygen
molecules (the oxygen we breathe) forming nitrogen dioxide. |

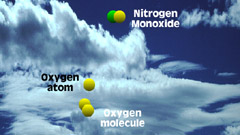
NO2 + light -> NO + O
|
3 - Then ultraviolet radiation
from the sun causes nitrogen dioxide to photochemically break up or
decompose freeing one of the oxygen atoms leaving nitric oxide and
atomic oxygen. |
O + O2 -> O3
|
4 - Atomic oxygen is very
reactive. In one reaction, it combines quickly with the oxygen we
breathe to produce ozone. |

O3 + NO -> NO2
+ O2
|
5 - In an unpolluted atmosphere,
ozone recombines with leftover nitric oxide again forming nitrogen
dioxide and oxygen. This neutralizes the ozone and prevents it from
building up. |
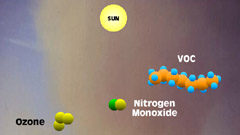 |
6 - But when the atmosphere
is polluted, unburned hydrocarbons or volatile organic compounds react
with the free nitric oxides and prevent them from recombining with
ozone. |
O3 + NO -> NO2
+ O2
|
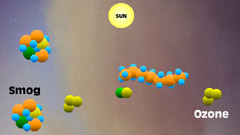
7 - When pollutants such
as volatile organic carbons are present, they gobble up the leftover
carbon monoxide before it can neutralize ozone, breaking the normal
cycle. |
 |
8 - The normal cycle is broken,
leaving ozone and photochemical byproducts behind. Ozone and smog
continue to accumulate. |
 |
Back to Pollutants Add
Up To Smog
|
